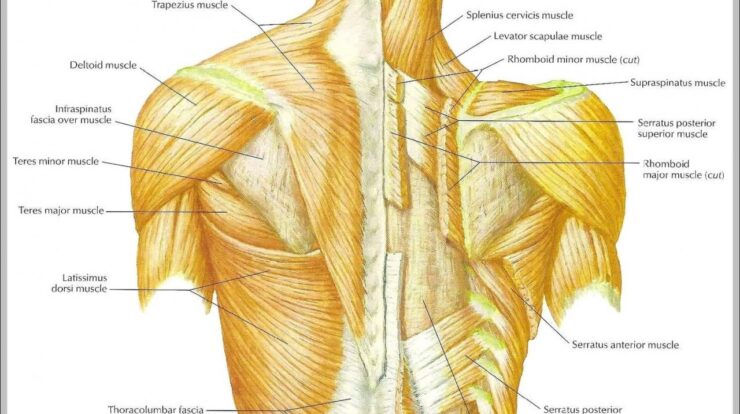
Back muscles, the unsung heroes of our bodies, play a crucial role in posture, movement, and respiration. From the mighty latissimus dorsi to the intricate rhomboids, these muscles work in harmony to support our spines, power our movements, and ensure we breathe effortlessly.
There are a number of things you can do to help relieve back pain caused by stiff and tight muscles. These include stretching, happy heavenly mother’s day , and strengthening exercises, and massage.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of back muscles, exploring their anatomy, exercises, common injuries, and the nutritional needs for their optimal health.
Stiff and tight back muscles can often lead to back pain. This is because these muscles are responsible for supporting the spine and pelvis, and when they are tight, they can put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the back, causing pain.
In addition, stiff and tight back muscles can also lead to poor posture, which can further contribute to back pain.
Anatomy of Back Muscles
The back muscles are a complex and interconnected group of muscles that support the spine, enable movement, and facilitate respiration. Understanding their anatomy is crucial for comprehending their functions and roles in overall physical health.
If you’re experiencing back pain, it could be due to stiff and tight back muscles . Tight muscles can restrict movement and put pressure on nerves, leading to pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes of back pain can help you find effective treatments and preventive measures.
The major back muscles include:
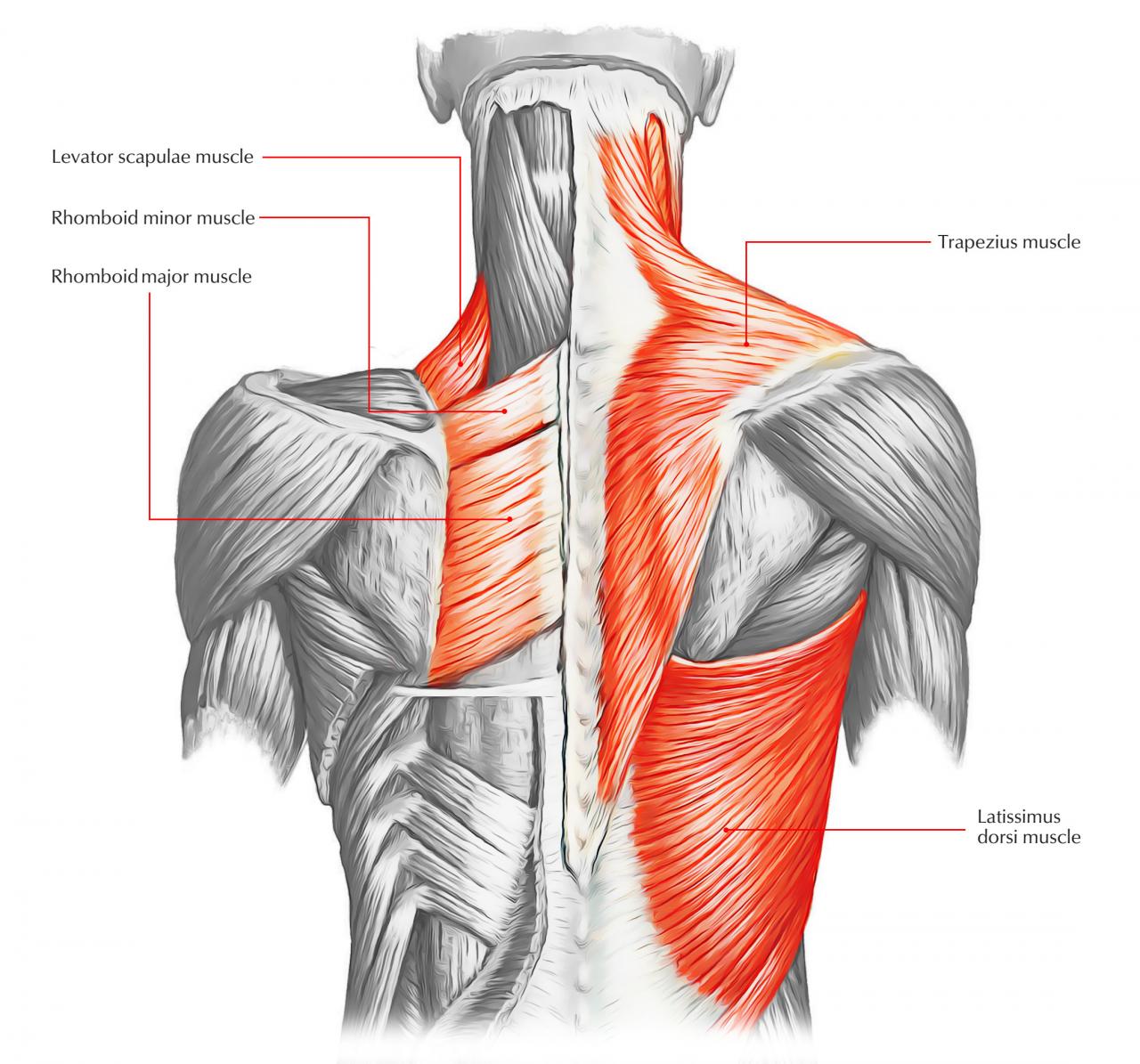
- Latissimus dorsi:A large, triangular muscle located on the sides of the back. It extends from the lower spine to the armpit and is responsible for pulling the arm down and back.
- Trapezius:A trapezoidal muscle extending from the base of the skull to the middle of the back. It is involved in shoulder movements, such as shrugging and rotating the head.
- Rhomboids:A group of three muscles located between the shoulder blades. They retract the shoulder blades and assist in stabilizing the spine.
These muscles work in concert to maintain proper posture, support the spine, and facilitate movements such as bending, twisting, and lifting.
Today is a day to celebrate all the mothers who have passed away, especially those who have left a lasting impact on our lives. We remember their love, their sacrifices, and their unwavering support. Happy Heavenly Mother’s Day to all the mothers who are now angels in heaven.
Exercises for Back Muscles
Strengthening and developing the back muscles is essential for overall fitness and posture. Here are some effective exercises to target these muscles:
- Pull-ups:A compound exercise that targets the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and rhomboids. Perform by hanging from a bar and pulling yourself up until your chin reaches the bar.
- Barbell rows:A variation of the pull-up that allows for added weight. Sit with your feet flat on the floor and hold a barbell in front of your thighs. Bend forward at the hips and row the barbell towards your chest.
- Deadlifts:A full-body exercise that targets the lower back muscles, including the erector spinae and hamstrings. Stand with your feet hip-width apart and bend forward at the hips to lift a barbell from the floor.
Incorporating these exercises into a fitness routine can help improve posture, reduce back pain, and enhance overall strength and functionality.
Common Back Muscle Injuries
Back muscle injuries are common and can range from mild strains to severe herniated discs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and recovery.
For those who want to express their love and gratitude to their mothers in German, here’s a special message: Alles Gute zum Muttertag !
- Strains:Overstretching or tearing of a muscle, often caused by excessive force or poor technique. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and muscle spasms.
- Sprains:Overstretching or tearing of a ligament, the connective tissue that joins bones together. Symptoms are similar to strains but may also include swelling and bruising.
- Herniated discs:A condition where the soft, gelatinous center of an intervertebral disc pushes through its outer layer. Symptoms can include severe pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs or arms.
Treatment for back muscle injuries typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), followed by physical therapy and strengthening exercises.
If you’re experiencing back pain, it could be due to stiff and tight back muscles . Tight muscles can restrict movement and put pressure on nerves, leading to pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes of back pain can help you find effective treatments and preventive measures.
Back Muscle Rehabilitation: Back Muscles
Rehabilitating back muscle injuries involves a comprehensive approach that addresses pain management, mobility restoration, and strength rebuilding.
A typical rehabilitation program includes:
- Stretching:Gentle stretching exercises help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
- Strengthening:Gradually increasing the intensity of strengthening exercises to rebuild muscle strength and stability.
- Stabilization:Exercises that focus on core and back muscles to enhance spinal stability and reduce the risk of re-injury.
Rehabilitation should be supervised by a healthcare professional to ensure proper form and progression.
Back pain is a common problem that can be caused by a number of factors, including stiff and tight muscles. Back muscles can become stiff and tight due to overuse, injury, or poor posture. When these muscles are tight, they can put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the back, which can lead to pain.
Nutrition for Back Muscle Health
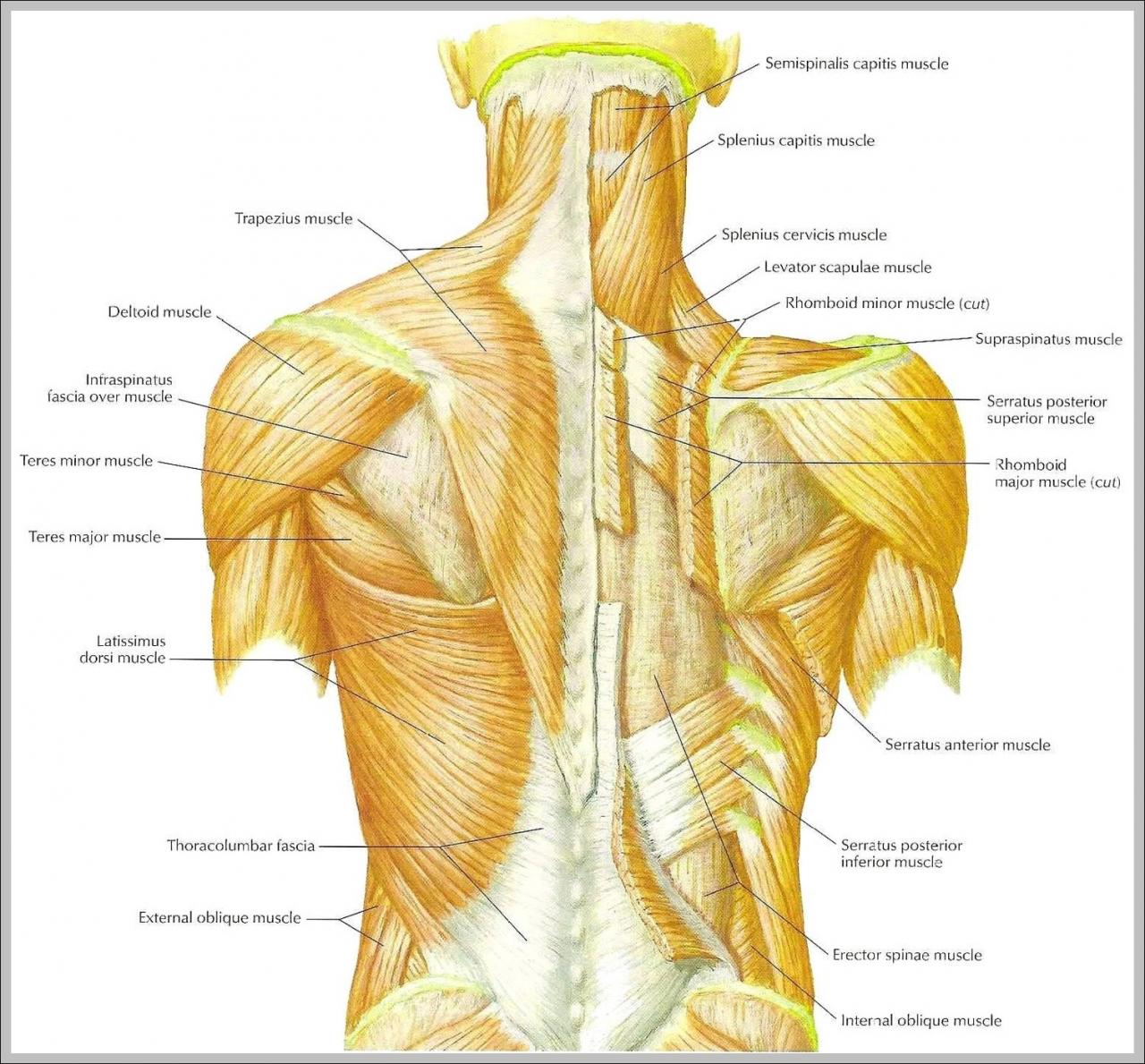
Adequate nutrition is essential for supporting back muscle health and recovery. A balanced diet should include:
- Protein:Protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair. Good sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and lentils.
- Carbohydrates:Carbohydrates provide energy for muscle activity. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources.
- Essential nutrients:Vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium, play a role in bone health and muscle function.
Consuming a nutrient-rich diet helps promote back muscle recovery and growth, reducing the risk of injuries and supporting overall physical well-being.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, back muscles are essential for our overall well-being. Understanding their anatomy, performing targeted exercises, preventing injuries, and nourishing them with proper nutrition are key to maintaining a strong and healthy back. Remember, a healthy back is a happy back, so let’s give these unsung heroes the attention they deserve.
Happy Heavenly Mother’s Day to all the mothers who are no longer with us. We may not be able to physically celebrate with them, but we can still remember them and the love they gave us. How can stiff and tight muscles result in back pain ?
FAQ Section
What are the most common back muscle injuries?
Strains, sprains, and herniated discs are among the most prevalent back muscle injuries.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Maintain good posture, lift weights properly, and engage in regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
What foods are good for back muscle health?
Lean protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide essential nutrients for muscle recovery and growth.
